WEEK 3 (DATA COMMUNICATION)
DATA COMMUNICATION ?
-Data Communications is the transfer of data or information between a source and a receiver. The source transmits the data and the receiver receives it. The actual generation of the information is not part of Data Communications nor is the resulting action of the information at the receiver. Data Communication is interested in the transfer of data, the method of transfer and the preservation of the data during the transfer process.-Data communication is, vey simply, the collection and disrtibution of the electronic representation of information from and to remote facilities by means of electrical transmission systems such as telephone lines, satellites or coaxial cable. The information can appear in a variety of formats; data, text, voice, still pictures, graphics and vedio. Prior to transmission, the raw information must be digitised.
WHAT IS "MODEM" ???
-Modems are often used to enable computers to communicate with each other across telephone lines. A modem converts the digital signals of the sending computer to analog signals that can be transmitted through telephone lines. When the signal reaches its destination, another modem reconstructs the original digital signal, which is processed by the receiving computer.
To convert a digital signal to an analog one, the modem generates a carrier wave and modulates it according to the digital signal. The process of receiving the analog signal and converting it back to a digital signal is called demodulation. The word "modem" is a contraction of its two basic functions: modulation and demodulation.
COAXIAL CABLE ??
-Coaxial Cable consists of 2 conductors. The inner conductor is held inside an insulator with the other conductor woven around it providing a shield. An insulating protective coating called a jacket covers the outer conductor.
The outer shield protects the inner conductor from outside electrical signals. The distance between the outer conductor (shield) and inner conductor plus the type of material used for insulating the inner conductor determine the cable properties or impedance. Typical impedances for coaxial cables are 75 ohms for Cable TV, 50 ohms for Ethernet Thinnet and Thicknet. The excellent control of the impedance characteristics of the cable allow higher data rates to be transferred than Twisted Pair cable.
OPTICAL FIBRE??
-Optical Fibre consists of thin glass fibres that can carry information at frequencies in the visible light spectrum and beyond. The typical optical fibre consists of a very narrow strand of glass called the Core. Around the Core is a concentric layer of glass called the Cladding. A typical Core diameter is 62.5 microns (1 micron = 10-6 meters). Typically Cladding has a diameter of 125 microns. Coating the cladding is a protective coating consisting of plastic, it is called the Jacket.
AMPLITUDE,PERIOD AND FREQUENCY..
Analog signal on the other hands, is like the human voice. It is formed by continuously varying voltage levels that create a wave that can be grasped by an analogue transmitter like microphone. This analogue signal features involves 2 parameters, which are frequency and amplitude as shown in figure.
Amplitude (A): how high the peaks are or how low the troughs are, in meters.
The displacement is how far the wave vibrates / oscillates about its equilibrium (center) position.
Amplitude is correlated with the total energy of the system in periodic motion. Larger amplitude = greater energy.
Period (T): the time it takes for one cycle, in seconds.
Frequency (f): the rate, or how many cycles per second, in Hertz (cycles per second).
DATA TRANSMISSION ???
 Digital transmission is the language of computer. The physical connection determines how many bits (1's or 0's) can be transmitted at a single instance of time. If only 1 bit of information can be transmitted over the data transmission medium at a time then it is considered a Serial Communication.
Digital transmission is the language of computer. The physical connection determines how many bits (1's or 0's) can be transmitted at a single instance of time. If only 1 bit of information can be transmitted over the data transmission medium at a time then it is considered a Serial Communication.
Digital signal need to be changed into analogue signal to be transmitted through PSTN lines that act as the media transmission.the process of changing analogue to digital signal is called modulation and process of changing its back to the analogue form is called demodulation. MoDem is the hardware that used in computer to do this process.
WHAT IS DATA FLOW ???
2) HALF DUPLEX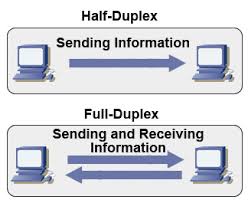
3) FULL DUPLEX
WHAT IS DATA FLOW ???
-Data flow is the flow of data between 2 points. The direction of the data flow can be described as:
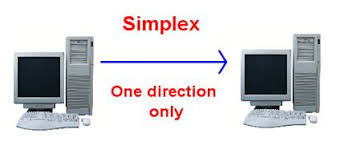
1) SIMPLEX
-Simplex: data flows in only one direction on the data communication line (medium). The role of the transmitter and the receiver are fixed. Examples are Radio and Television broadcasts. They go from the TV station to your home television.
2) HALF DUPLEX
-data flows in both directions but only one direction at a time on the data communication line. One station transmitts information to anoyher station without any interruption. Examples, conversation on walkie-talkies is a half-duplex data flow. Each person takes turns talking. If both talk at once so that will not occur!
3) FULL DUPLEX
-Data flows in both directions simultaneously. Its consists of two simplex channels are channel is used to forward while the other as the reversal channel, linking at the same point. Modems are configured to flow data in both directions.

your blog a litle bit like mine one...like it..haha
ReplyDelete